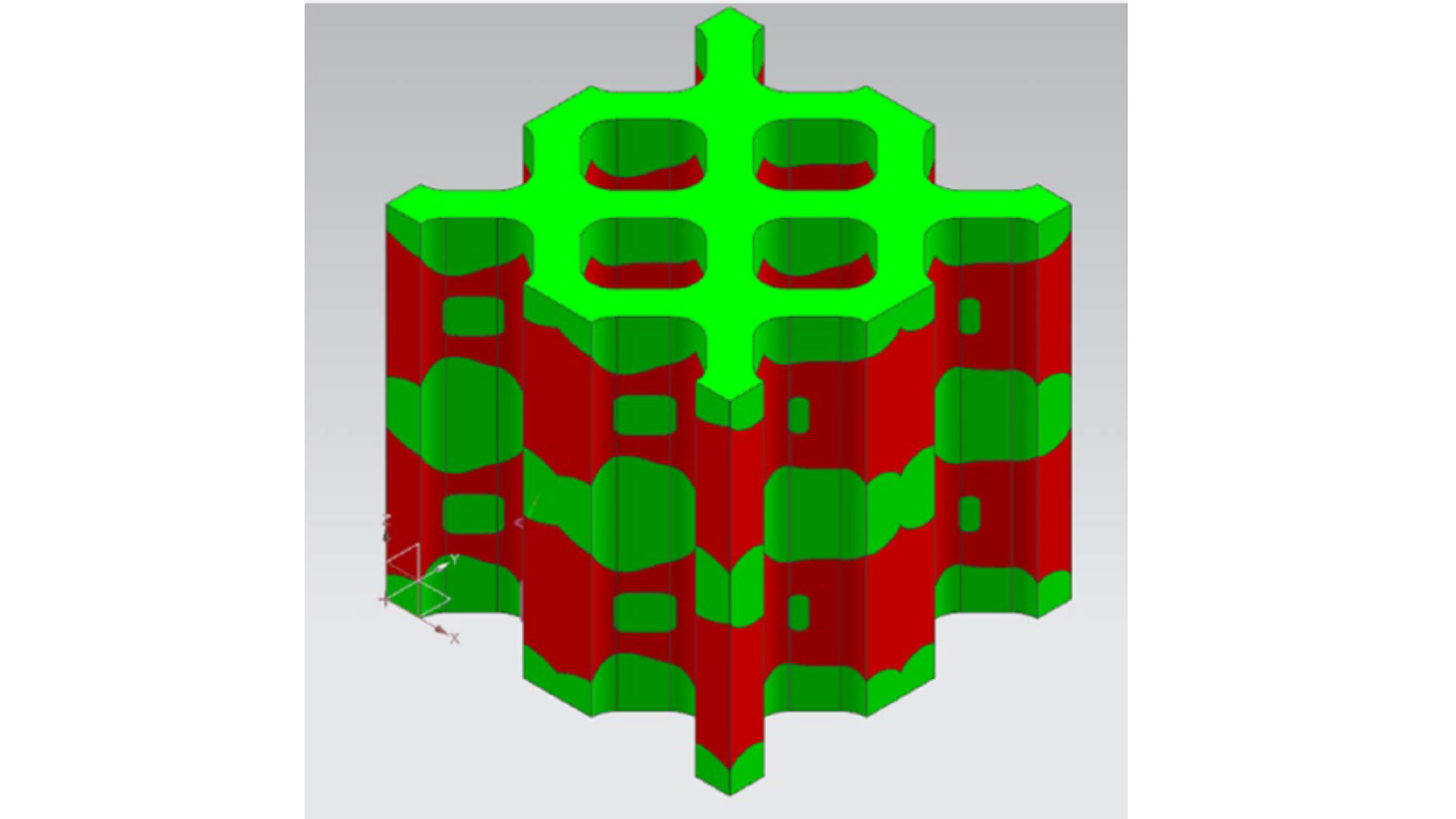
With a need to optimize weight to fly ratios, aerospace manufacturers are looking to using lattice structures produced with additive manufacturing. Designing lattice structures that also meet mechanical and performance requirements is very complex. Taking it a next step enabled by systems that can print with multiple materials increases the complexity. Newly published research shows design for additive manufacturing (DfAM) approaches that can be used to optimize cell geometry in lattice structures to achieve high mechanical stiffness, a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), and low thermal conductivity.
Researchers at the University of Cincinnati Center for Global Design and Manufacturing recently published their research to integrate of DfAM with multi-material topology optimization of lattice structures for optimized thermal and mechanical properties. Appearing in the April 2022 issue of ASME’s Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering. To support the additive manufacturing community, ASME is making the paper free to download through the end of April 2022.
DOWNLOAD NOW


